Flow lamination
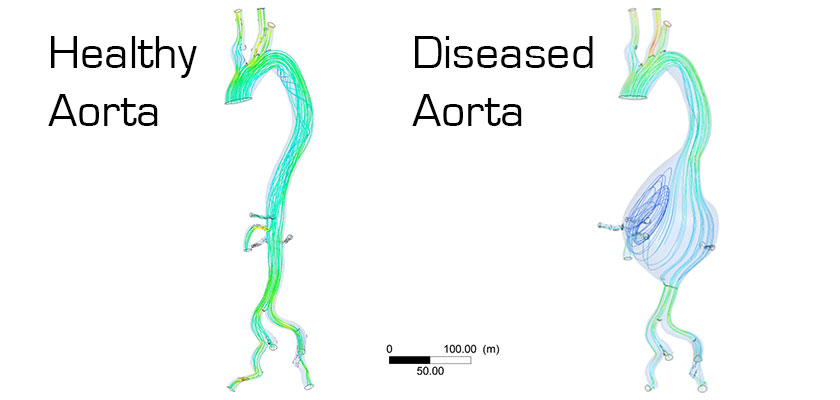
Healthy physiological flow Aneurysm with pathophysiological flow
In an aneurysm, the recirculating blood flow, driven by the change in shape of the artery itself, becomes pathophysiological.
The consequent weakening and enlargement and further change in shape of the wall can lead to rupture.
The MFM is constructed of three-dimensional braided wire mesh. As blood passes through the porous layers of the MFM, the flow becomes laminar, streamlined along the artery wall.
Converting Recirculating Flow into a Laminar Flow
The MFM promotes a physiological remodeling of the flow inside the aneurysm while maintaining branch patency.
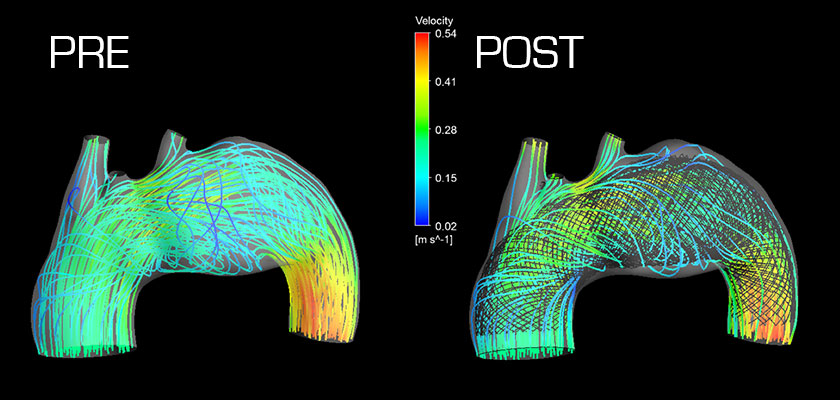
Pathophysiological blood flow before MFM implantation Restoration of regular laminar blood flow after MFM implantation
réf Stefanov F. Insights from complex aortic surgery with a streamliner device for aortic arch repair (STAR), The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2016), doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.06.043
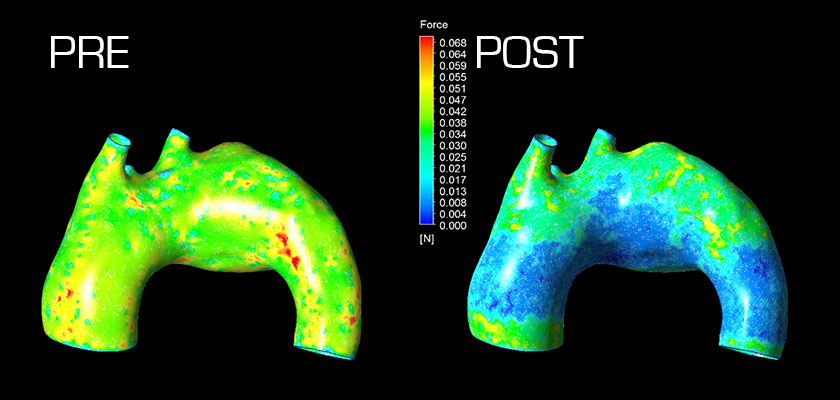
Peak wall shear stress prior to MFM implantation Reduced wall shear stress after MFM implantation
Through lamination of blood flow and the elimination of vortices, the shear stress along the artery wall is reduced and further weakening prevented, relieving the risk of rupture .
réf Stefanov F. Insights from complex aortic surgery with a streamliner device for aortic arch repair (STAR), The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2016), doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.06.043
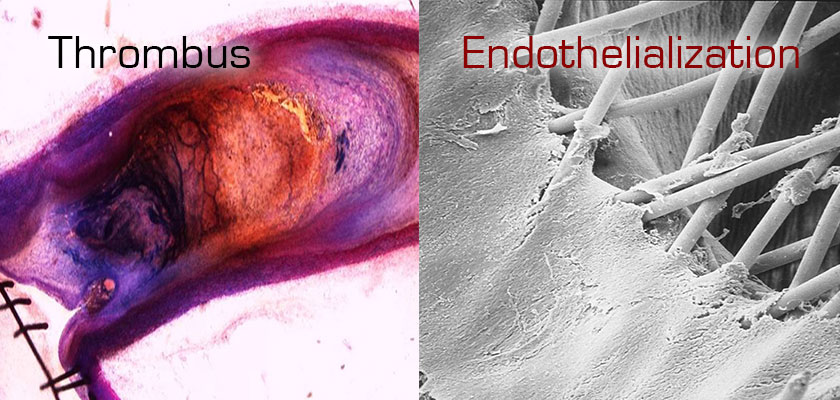
The laminar flow promotes formation of an organized thrombus while also inducing the formation of endothelial tissue on the MFM and on the artery wall.
réf Sultan, S., Kavanagh, E. P., Alves, A., Wanke, I., Goericke, S., Ruefenacht, D., & Hynes, N. (2015). A Pilot Study of the Intracranial Multilayer Flow Modulator as a New Disruptive Technology in the Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms. (3). doi:10.18103/mra.v0i3.157
réf SEM: In Vivo Histology Study No. 500-44 “Histological and Ultra-structural analysis of 2 explanted aortic stents” – Biomatech, NAMSA France – ISO17025.
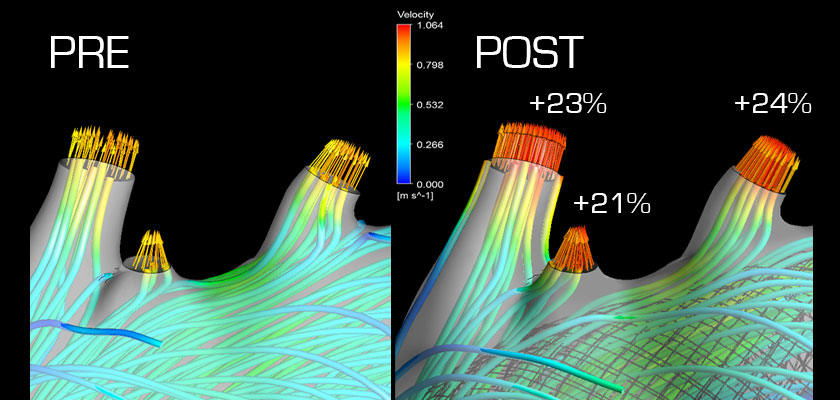
Compromised branch artery perfusion before MFM implantation Enhanced branch artery perfusion after MFM implantation
The MFM design significantly enhances the perfusion of organs,
thereby avoiding serious ischemic complications and improving quality of life.
réf Stefanov F. Insights from complex aortic surgery with a streamliner device for aortic arch repair (STAR), The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2016), doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.06.043
Computational fluid dynamics modeling of blood recirculation inside the aneurysm before MFM implantation (left) and the lamination of blood flow after MFM implantation (right).